RM
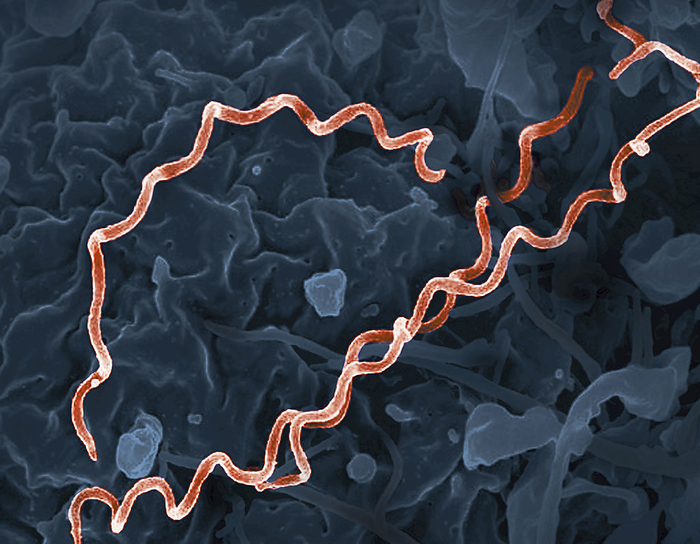
Treponema pallidum syphilis bacteria, SEM
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) image of Treponema pallidum (red), the bacteria that cause syphilis. T. pallidium is a gram-negative, spirochaete bacterium which is an obligate human parasite, meaning it cannot complete its life cycle without a human host. Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) which causes ulceration and rashes initially. If left untreated, tertiary syphilis may develop following a latency period, causing potentially fatal organ damage., by NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH, NIAID/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

More
Top Categories
