RM
Enhanced rock weathering, illustration
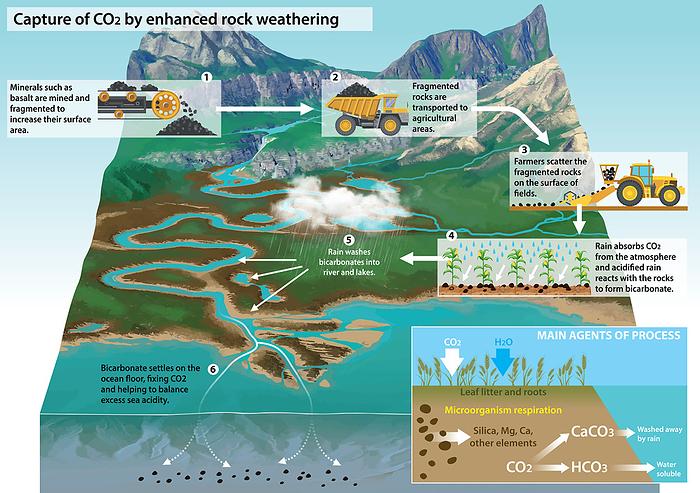
Illustration showing a proposed mechanism for capturing atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) and locking it away for a few thousand years. Known as enhanced rock weathering, it is a method of accelerating the natural weathering of rocks that occurs as part of the natural carbon cycle. Volcanic rocks are ground up to increase their reactive surface area and spread on agricultural land. When rain, which contains carbon dioxide absorbed from the atmosphere, falls on the rocks, the two react to form bicarbonate. The bicarbonate is washed into rivers and then into the sea where it is used to form shells and skeletons that will eventually sink to the ocean floor. If enough CO2 could be removed from the atmosphere the effects of climate change could be mitigated., by JOSE ANTONIO PENAS/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

More
Top Categories
