RM
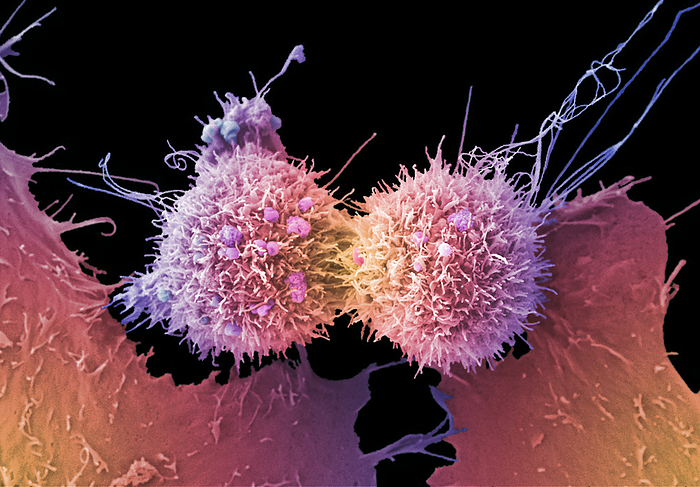
Cervical cancer cells dividing, SEM
Cervical cancer cell, coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM). The cervix is the lower part of the womb, also called the neck of the womb, and comprises part of the woman's reproductive system. Cervical cancer is more common in younger women. One of the main causes of cervical cancer is a persistent infection of certain types of human papilloma virus (HPV). In this image the central cells are undergoing cell division which is where the parental cell divides into two daughter cells. Cancer cells often divide and multiply uncontrollably which can lead to the formation of tumours. These cells also have long extending filopodia like structures. Filopodia contain actin filaments and can have roles in numerous processes including cell-cell interactions, cell migration or as a sensory guide towards a chemoattractant, which is a chemical agent that induces a cell to migrate towards it. There is also a small amount of blebbing. Blebbing is a bulge or protrusion of the plasma membrane of the cell which is visible on the cell surface. Blebbing may occur for a number of different reasons including during apoptosis, or if a cell is undergoing physical or chemical stress. It also has important functions in cellular processes such as cell division and cell locomotion, playing a role in cell migration. Magnification: x2800 when printed at 10 cm wide., by ANNE E. WESTON/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

More
Top Categories
