RM
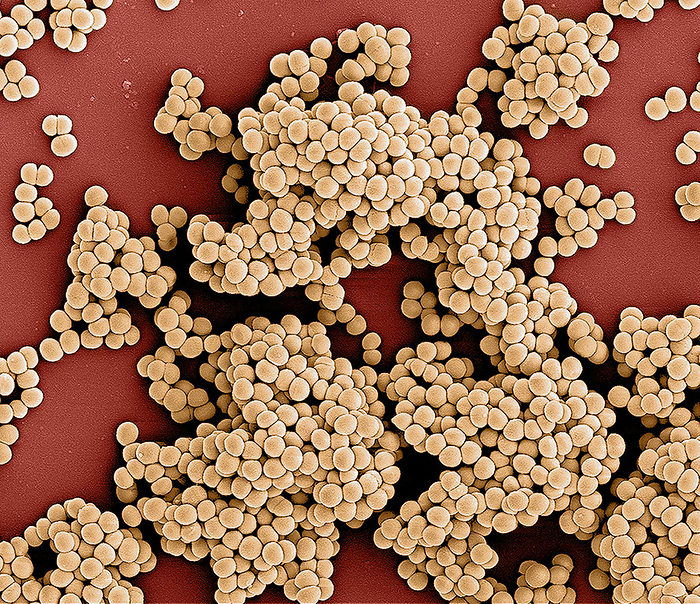
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureusbacteria, SEM
Coloured scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteria. MRSA is a gram-positive, round (coccus) bacterium. It is resistant to many commonly prescribed antibiotics. S. aureus is carried by around 30 percent of the population without causing any symptoms. In vulnerable people, such as those that have recently had surgery, it can cause wound infections, pneumonia and blood poisoning. Specific antibiotics, often administered intravenously, can be used to treat MRSA infections., by NIAID/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

More
Top Categories
