RM
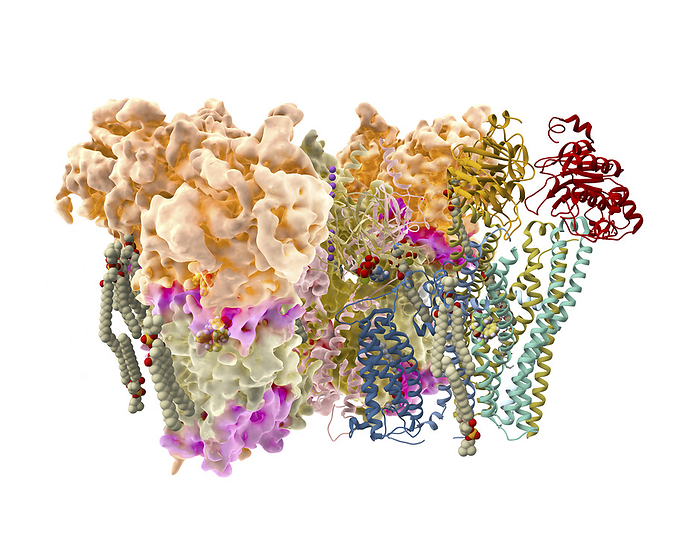
Repaglinide antidiabetic drug action, illustration
Illustration showing repaglinide (yellow, white, blue and red spheres, centre-left and centre-right) binding to an ATP-dependent potassium channel (multicoloured globular/helical structures) on a pancreatic beta cell. Repaglinide belongs to a class of drugs known as meglitinides which bind to this type of receptor on pancreatic beta cells, stimulating insulin release. Insulin, in turn, increases cellular glucose uptake, reducing blood sugar levels, making repaglinide a suitable treatment for type 2 diabetes., by RAMON ANDRADE 3DCIENCIA/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

More
Top Categories
