RM
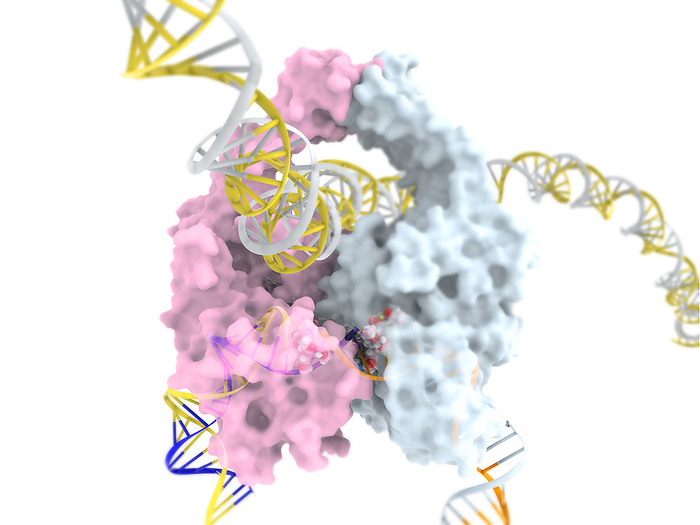
Anticancer drug etoposide inhibiting topoisomerase II, illustration
Illustration of the enzyme human topoisomerase II (white/pink, globular) undoing the overcoiling of DNA (deoxyribonuclease, yellow and blue/white helices) by cutting both strands, before re-ligating (re-joining) them once the coils have been relaxed. Etoposide (white, red and blue spheres) inhibits the re-ligation phase of the uncoiling process. This leaves broken DNA strands which can not undergo replication, making affected cells vulnerable to apoptosis (controlled cell death). Cancer cells replicate rapidly and in an uncontrolled manner. By inhibiting a crucial part of cell replication, etoposide can slow the growth of tumours and induce their destruction by apoptosis., by RAMON ANDRADE 3DCIENCIA/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY

More
Top Categories
